Performance
이 포스트는 cpu 성능 측정하는 방법에 대해 설명한다.
Performance Metrics #1: Time
- wall-clock time, response time, or elapsed time: 실제로 걸린 시간을 의미한다.
- cpu (execution) time: CPU time spent for a given program, user CPU time + system CPU time
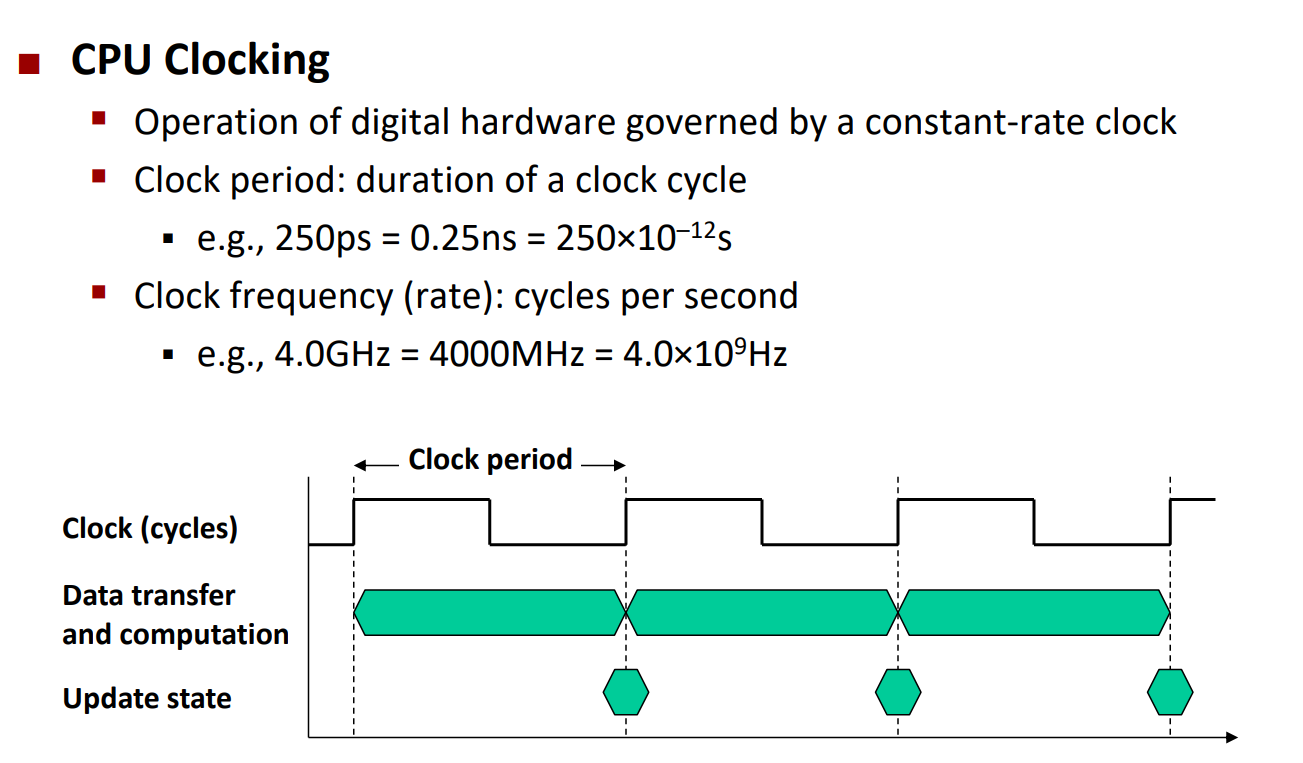 이중 CPU time을 더욱 깊게 파보자.
이중 CPU time을 더욱 깊게 파보자.
CPU는 clock을 통해 동기적으로 작동한다. (synchronous)
- clock period: clock 한번 올라 갔다 내려오고 다시 올라가기 까지의 시간
- clock frequency(rate): clock period 역수, cycles per second
Iron Law of CPU Performance
\(\begin{aligned} CPU time =& \frac{Seconds}{Program} \newline =& \frac{Cycles}{Program} \times \frac{Seconds}{Cycle} \newline =& \frac{Instructions}{Program} \times \frac{Cycles}{Instruction} \times \frac{Seconds}{Cycle} \end{aligned}\)
여기서 Instructions per Program 은 program이나 compiler에 따라 결정되는 것이고
Cycles per Instruction(CPI)가 CPU hardware에 따라 결정되는 부분이다.
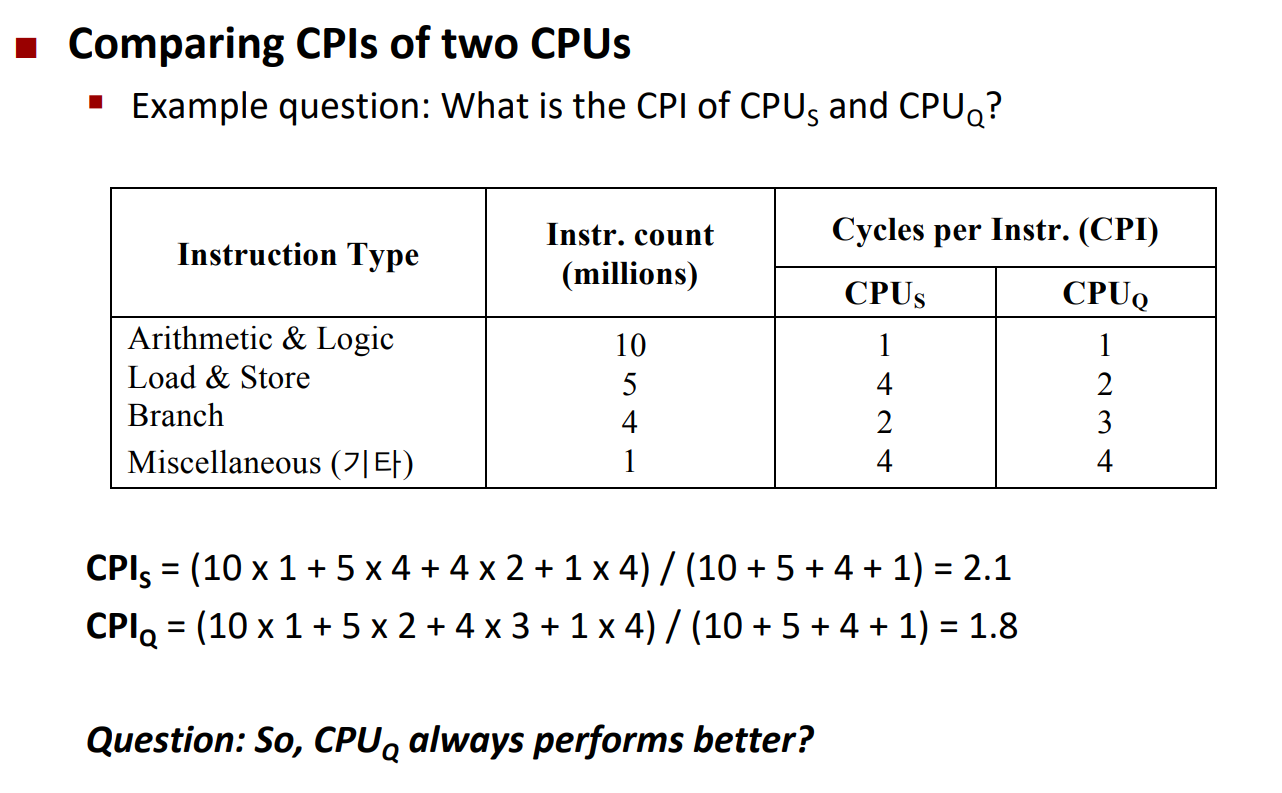 이러한 방식으로 CPI를 계산한다. 그럼 CPI가 작은게 항상 좋은가?
이러한 방식으로 CPI를 계산한다. 그럼 CPI가 작은게 항상 좋은가?
그건 모른다. 마지막에 clock period도 곱해줘야하고 각 program 마다 instruction 수도 다를거고 암튼 항상 좋은 건 아니다.
Performance Metrics #2: Rate
MIPS(million instructions per second)
\(MIPS = \frac{Instruction\space count}{Execution\space time\times 10^6}\) 보통은 MIPS가 높으면 좋다.
MFLOPS(million floating-point operations per second)도 있다.