baekjoon 1931:회의실 배정
1931번 회의실 배정
접근
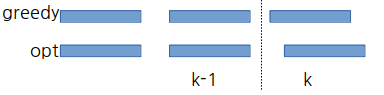
k-1번째까지만 greedy랑 optimal solution이랑 같다고 해보자.
greedy는 항상 일찍 끝나는 것을 고르니 optimal solution의 k번째 회의보다 더 먼저 끝나는 k번째 회의를 가지고 있을 것이다.
그런데 optimal solution의 k번째를 greedy의 k번째로 바꿔도 더 먼저 끝나기 때문에 뒤에 따라오는 k+1, k+2번째에 영향을 주지 않고
총 회의 개수는 무조건 동일하게 유지된다. 그럼 greedy도 opt sol이 될 수 있는 것이고
따라서 greedy랑 optimal solution이랑 k번째까지만 같다는 것은 모순이다.
코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool compare1(pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) { //vector의 비교 함수를 따로 제작하였다.
if (a.second < b.second) {
return true;
}
else if (a.second == b.second) {
return a.first < b.first;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n; cin >> n;
vector<pair<int, int>> v;
while(n--){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
v.push_back({a, b});
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), compare1); //먼저 끝나는 회의를 고르기 위해 끝나는 시간 기준 오름차순으로 미리 회의를 정렬한다.
int count = 0;
int endtime = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){
if(endtime <= v[i].first){
count++;
endtime = v[i].second;
}
}
cout << count;
return 0;
}
배운 점
greedy알고리즘 실제 구현해보고, vector 정렬 함수 따로 제작 해서 하는 방법을 배웠다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.